- +91-7701965089
- drrajeshtalwar@hotmail.com
- New Delhi
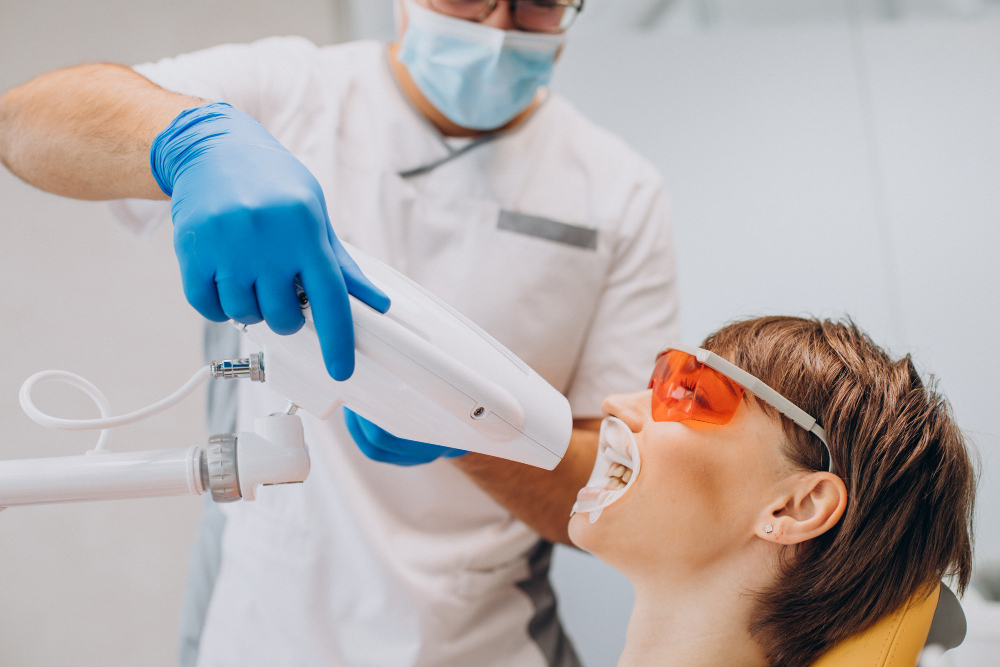
Bleaching is a chemical process used to lighten or remove color from materials such as fabrics, hair, teeth, or even water and paper. The primary goal of bleaching is to achieve a cleaner, whiter appearance by breaking down the color-causing compounds.
There are two main types of bleaching agents: oxidizing and reducing. Oxidizing agents, such as chlorine and hydrogen peroxide, work by breaking the chemical bonds of chromophores (color molecules), making them colorless. Reducing agents, like sulfur dioxide, work by removing oxygen from the color molecules, altering their structure and appearance.
In textile and paper industries, bleaching is essential to produce white fabrics and paper by removing natural pigments and impurities. In cosmetics and personal care, hair bleaching uses hydrogen peroxide or ammonia to lighten hair by removing its natural pigment, melanin. Teeth bleaching is a popular dental procedure that uses safe peroxide-based agents to whiten teeth stained by food, drinks, or smoking.
Bleaching is also used in water treatment and sanitization. Chlorine bleach is commonly used as a disinfectant in households and hospitals due to its ability to kill bacteria and viruses.
While bleaching is highly effective, it must be used with care. Over-bleaching can weaken materials, irritate skin, or cause environmental harm if not handled properly. Therefore, protective measures and appropriate concentrations are important for safety.